The 6G-SANDBOX

6G-SANDBOX is a European research project and infrastructure designed to support an experimentation ecosystem for next-generation technology and research validation needed for the emerging 3PPP 6G communications standard. The 6G-SANDBOX targets technologies and research that span the entire 6G service provisioning chain, with reference to user/data, control and management planes. The 6G-SANDBOX implements a series of "Trial Networks" - configurable, manageable and controllable end-to-end networks, composed of both digital (software-only) and physical nodes.
Key Features
Pan-European Testbed: 6G-SANDBOX offers a distributed infrastructure with experimental platforms in Malaga (Spain), Berlin (Germany), Oulu (Finland), and Athens (Greece), allowing organizations and researchers to conduct trials on advanced network technologies.
Trial Networks: The project introduces the concept of “Trial Networks,” which are fully configurable, manageable, and controlled end-to-end networks made up of both digital and physical nodes. These networks enable realistic testing and validation of new 6G concepts and technologies.
Open Experimentation: The facility is open to third parties, including external experimenters selected via open calls, providing automated experimentation capabilities and a rich toolbox for testing a wide range of 6G enablers.
Focus Areas: 6G-SANDBOX targets a broad spectrum of technological advances, including zero-touch management, flexible multi-tenancy architectures, network intelligence, security, digital twins, artificial intelligence (AI), and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces.
Support for 5G-Advanced and 6G: While primarily focused on 6G, the testbed also supports validation of 5G-Advanced features, ensuring a smooth transition and backward compatibility.
Example Use Cases and Scenarios
Connected vehicles and smart transportation
Smart agriculture (Agro 5G)
Urban infrastructure (smart cities, ports, and campuses)
Real-world RIS deployments and satellite integration
Locales
The 6G-SANDBOX Trial Networks incorporates test nodes distributed across the EU, in Athens Greece, Berlin Germany, Malaga Spain, and Oulu Finland.

6G-SANDBOX Objectives
After the successful deployment of 5G networks, network operators, client device manufacturers and other ecosytems participants are fleshing out the principles of 6G networks and services. At the same time, government and industry anticipate a positive disruptive socioeconomic impact from the 6G rollout.
This potential of and need for experimentation facilities was validated already with the 5G rollout, where 5G pan-European facilities (such as 5GENESIS, 5G-VINNI, and 5G-EVE), supported 5G digital transformation and trial of innovative applications and services. For 6G, the need for experimentation facilities is further amplified beyond that of 5G, especially around development of experimental infrastructure, that will validate 6G technologies and use cases. As a response to this challenge, the 6G-SANDBOX project is dedicated to providing clear and tangible contributions towards an experimentation ecosystem for 6G in Europe.
Summary of Objectives
To establish a robust experimentation ecosystem for 6G in Europe.
To validate and accelerate the industrial adoption of innovative network technologies.
To contribute to Europe’s leadership in the global race for 6G by supporting both academic and industrial research
The 6G-SANDBOX Architecture
Experimenters do not need proximate physical access to any of the SANDBOX sites unless the systems under test involve physical component(s). Even in experiments involving physical devices (e.g., handsets and other local nodes), once a device is installed and the trial network instantiated, experimenters can run tests remotely over VPNs, with the assistance of an engineer at the given site if needed. In most use cases, the infrastructure can support physical and virtual equipment, as needed, end-to-end.
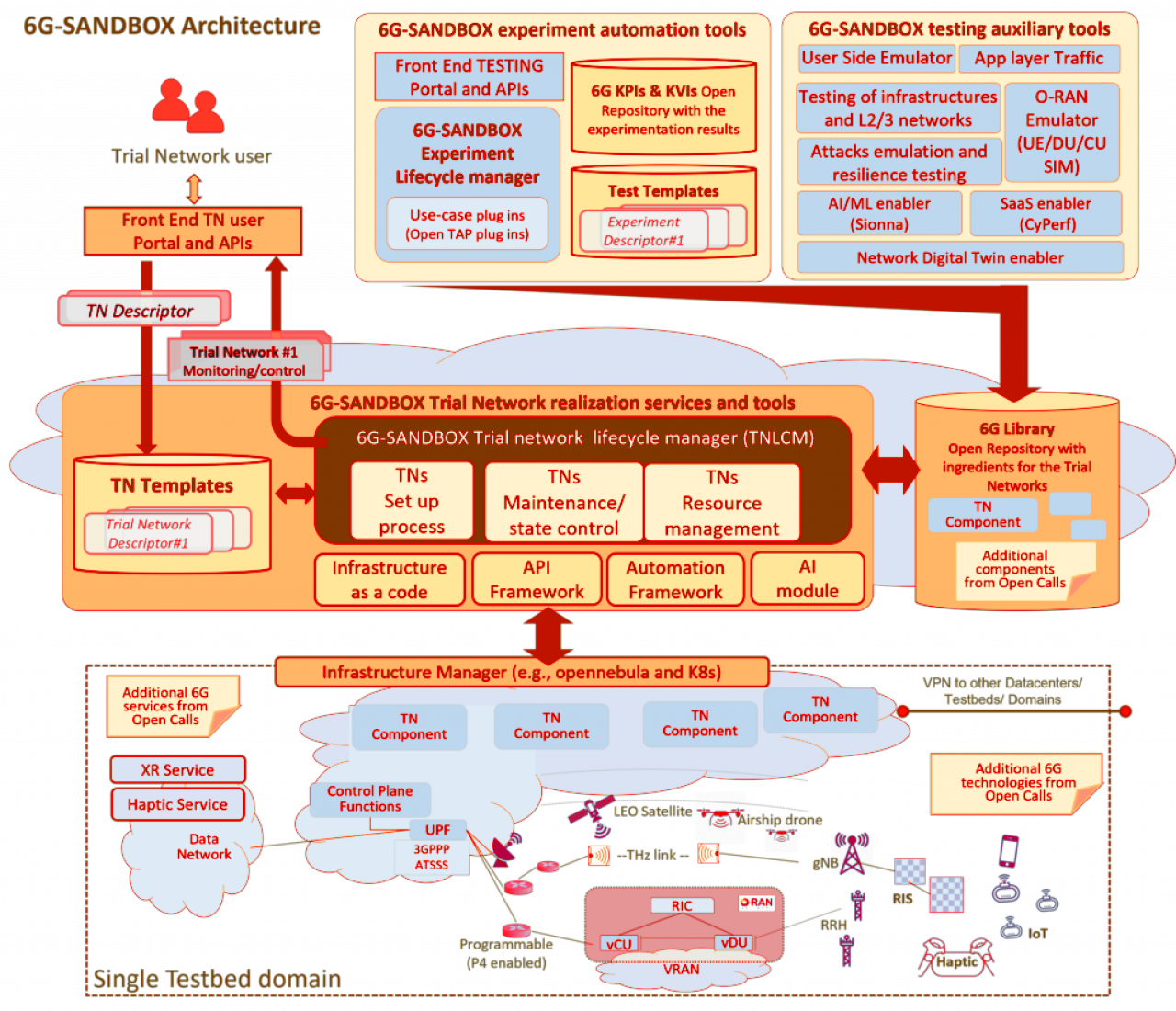
Learn more about the 6G-Sandbox at https://6g-sandbox.eu/
The Role of OpenTAP
OpenTAP serves as a foundational automation and orchestration framework within the 6G-SANDBOX project. Its role is to enable automated, API-driven experimentation and lifecycle management across the distributed SANDBOX trial networks.
Key Functions of OpenTAP in the 6G-SANDBOX
Experiment Automation: OpenTAP provides the core engine that automates the setup, execution, and teardown of experiments on the 6G-SANDBOX platforms. This ensures repeatability, efficiency, and reliability in running complex 6G network trials.
API-Based Experimentation: The framework exposes APIs that allow experimenters to interact programmatically with the testbed, facilitating seamless integration with third-party tools and enabling experimentation-as-a-service.
Lifecycle Management: OpenTAP manages the full lifecycle of experiments, from resource allocation and configuration to monitoring, data collection, and results reporting.
Extensibility: Its modular architecture allows new technologies, devices, and test cases to be integrated easily, supporting the evolving needs of 6G research and validation.
Open Access and Reusability: By leveraging OpenTAP, 6G-SANDBOX ensures that experiment results, components, and APIs are reusable and accessible, contributing to the creation of a European 6G library and supporting open innovation.
Moreover, OpenTAP and Keysight commercial products built with OpenTAP play a central role in the 6G-SANDBOX.
All 6G-SANDBOX test plans are built with and for OpenTAP. OpenTAP was chosen for consistency and to provide a common unified approach across many (sub)projects. The selection of OpenTAP also reflects the preference for open source components in EU-sponsored projects.
6G-SANDBOX users and developers employ Keysight KS8400 and KS8500 environment to create, execute and analyze test plans.
Keysight Test Bench Architecture - Built on OpenTAP
At all four SANDBOX locales, OpenTAP, together with OpenTAP plugins and runners (see below), provide access to devices under test (DUTs) and enable remote/distributed execution of test loads and probes.
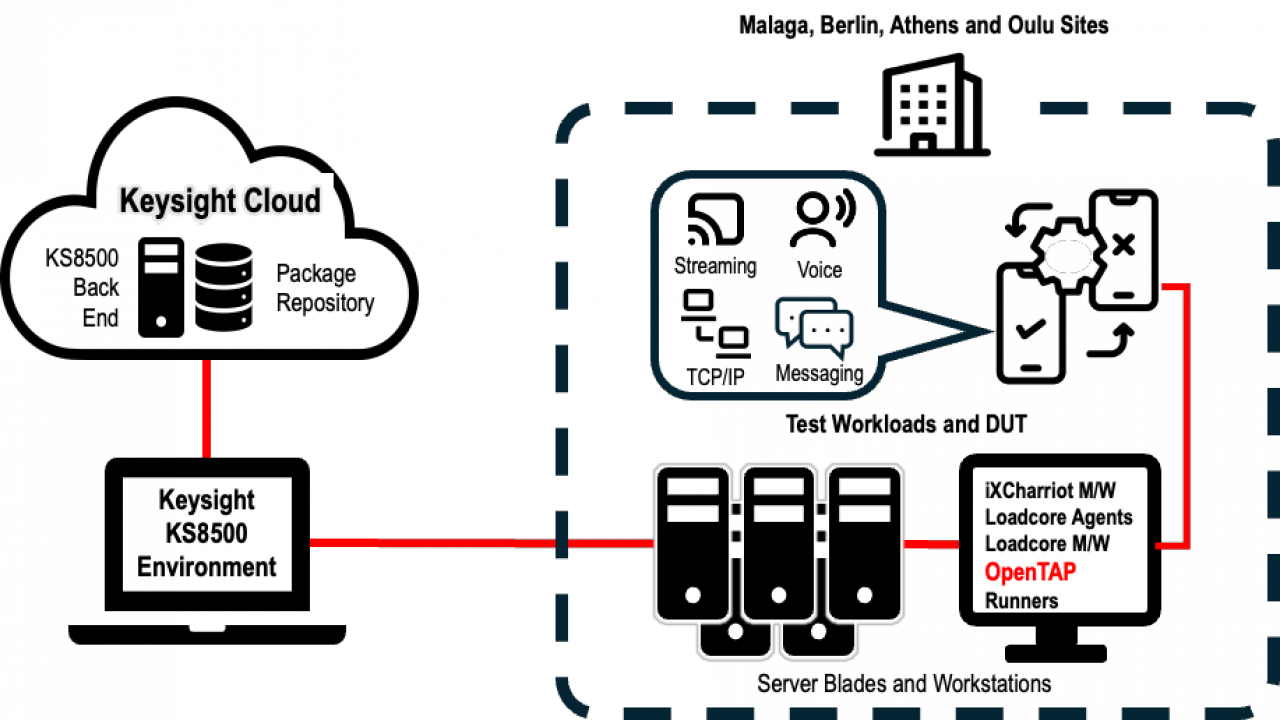
Plugins and Runners
A number of extensions to OpenTAP are needed to support core functionality in the 6G-SANDBOX architecture:
Loadcore - Automates 6G core network testing by simulating user equipment (UE) behavior and traffic generation. Loadcore validates network slicing, multi-access edge computing (MEC) deployments, and core network performance under load. Use cases include executing test plans to stress-test network slicing configurations or measure latency in MEC scenarios. Indeed, Loadcore has the capability to emulate all components in the network core through the use of agents, as well as putting them under test.
ixCharriot - Facilitates network performance testing (throughput, latency, jitter) by generating application-layer traffic across simulated or real network paths. IxChariot endpoints can be emulations or physical mobile/wireless devices. ixCharriot is embedded in OpenTAP test plans to automate QoS validation for 6G use cases like industrial IoT or ultra-reliable communications.
NE3 - Emulates 3GPP-compliant network elements (e.g., gNBs, AMF) to create controlled test environments. NE3 enables experiments by mimicking real-world network conditions (e.g., latency spikes, packet loss) during test automation workflows. NE supports protocol testing and edge computing scenarios, and is used for emulating network traffic impairments.
OpenTAP Runners - Specialized plugins within the 6G-SANDBOX architecture that facilitate remote execution of test plans and campaigns. Runners act as distributed agents that enable automated, remote execution of test plans across the 6G-SANDBOX infrastructure.
Dramatic Time Savings from OpenTAP
The testing described in this artcile was originally performed by hand, interfacing with the tools directly and processing data by hand. On average, per platform, running the tests, collecting and processing the results data took about a week. To cover the four platforms, the entire battery of tests would take up to a month.
Introducing OpenTAP into both the test execution and processing phases, the time required for the full battery of tests, per platform, was reduced to 16-20 hours. With the introduction of multiple runners that to mediate testing of all platforms simultaneously, a task that previously took a month could be completed in 24 hours

The 6G-SANDBOX Consortium
Today there are 18 commercial entities and universities involved int he 6G-SANDBOX project, including multiple European Keysight subsidiaries (in Belgium and Denmark), OpenTAP ecosystem partners (Nokia and Universidad de Malaga). See the complete list of Consortium members.

The Keysight Team
6G-SANDBOX is a European research project and infrastructure designed to support experimentation with next-generation technology and research validation needed for the emerging 3PPP 6G communications standard. The 6G-SANDBOX targets technologies and research that span the entire 6G service provisioning chain, with reference to user/data, control and management planes. This blog describes the SANDBOX and how it is enabled by OpenTAP.
Resources
The following resources are available for learning more about the 6G-SANDBOX






