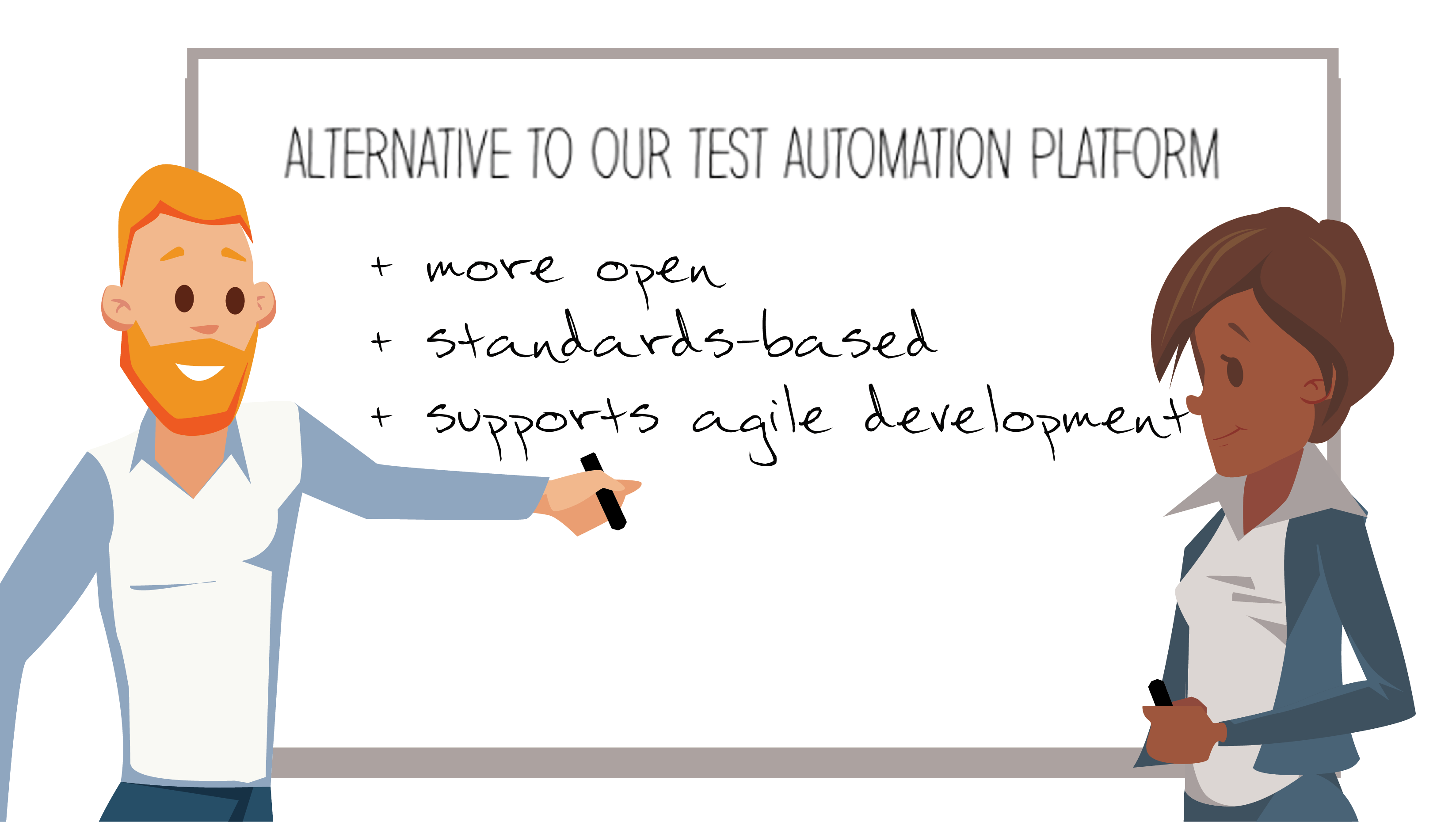
Use of AI in testing digital products is soaring, but human input remains hugely important. Testing managers express concerns about the need to accompany rapidly changing requirements, dealing with unstable testing environments, and insufficient time for adequate testing. This blog lays out the pluses and minuses of integrating AI into test design and testing workflows, and highlights when and where human oversight is required.